INTERACTION MOTIFS
In the following, we assume that you have downloaded the Rna3Dmotif binaries archive and uncompressed it according to the instructions given in the DOWNLOAD section.Listing the interaction motifs
Interaction motifs link one secondary structure element (internal, terminal, junction loop) to one or more helices and/or other secondary structure elements. The program designed to extract them is called Listim. It produces a Listing.
For example, suppose that you want to build the Listings of two structures:
- 23S rRNA of H. marismortui (PDB: 1S72, Chain: 0),
- Group II intron (PDB:3EOH, Chain:A).
After executing the Listim program, you get this result (see the User's Help for the notations used).
Identifying recurrent interaction motifs
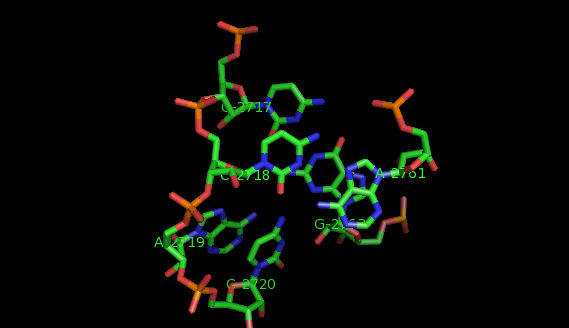
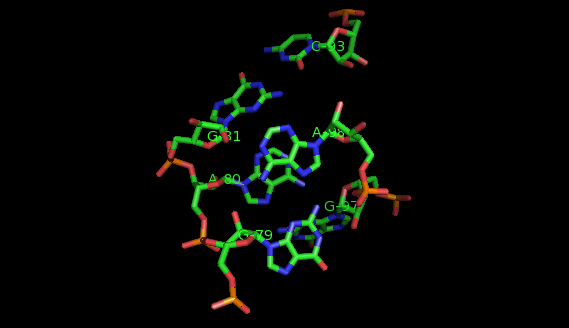
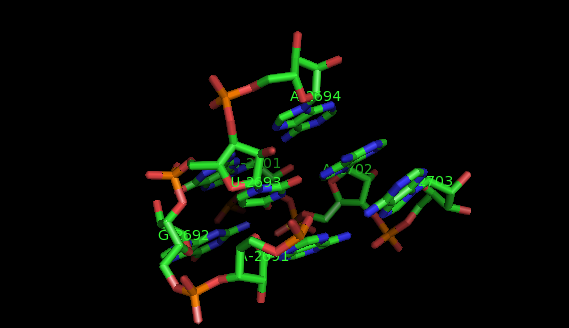
To identify recurrent interaction motifs present in two RNA chains, say 23S rRNA of H. marismortui (PDB: 1S72, Chain: 0) and a Group II intron (PDB:3EOH, Chain:A) you execute the Simintmot program. You get this spreadsheet file. You sort it by the last column (i.e. the non-canonic labels of the LJCNS) to get the clusters of potential recurrent motifs. For example, in our sorted file, these lines give the occurrences of a potential recurrent motif with the non-canonical labels "ffg". These occurrences must be superposed in 3D to make sure that they are biologically valid. In our example, 5 occurrences were successfully superposed. The motif in question is the A-minor motif (3 occurrences in 23S rRNA and 2 occurrence in GII intron).
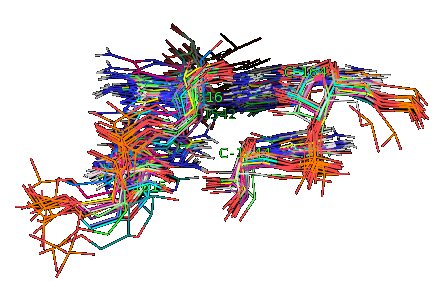
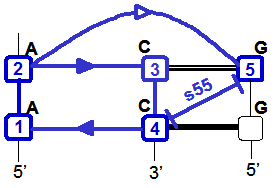
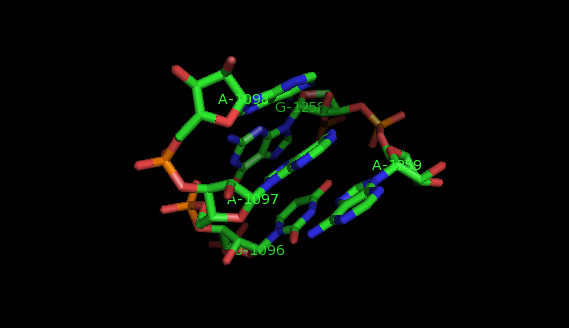
It may be of interest for the user to compare two specific interaction motifs. In this case, you invoke the Ljcns program which inputs two identifiers of interaction motifs and outputs, if it exists, their largest joint common non-canonical substructure (LJCNS) in the form of a mapping of the bases and basepairs. This program is useful to highlight similarities between two interaction motifs. For example, this mapping displays the structural similarities between an interaction motif in a ribonuclease P made of Sugar/Sugar interactions and an A-minor motif in 23S rRNA of H. marismortui.
|
|
|

|